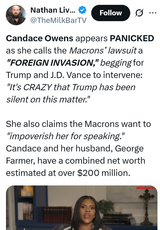
>>512503398
you can sue anyone in any court as long as that court has some kind of jurisdiction. You can sue a company in Califronia in an alabama court if you were in alabama or a resident of alabama when damages occurred to you caused by the company via faulty product or whatever.
These are the types of jurisdictions
1. Personal Jurisdiction:
This refers to a court's power over the parties involved in a case, ensuring they are properly brought before the court.
It determines whether the court has the authority to make a ruling that legally binds the individuals or entities involved.
For example, a court in California might not have personal jurisdiction over a person who lives in New York and has no connection to California.
2. Subject Matter Jurisdiction:
This type of jurisdiction determines whether a court has the power to hear a specific type of case.
Different courts are often assigned specific types of cases based on their jurisdiction. For example, a bankruptcy court has jurisdiction over bankruptcy cases.
A court lacking subject matter jurisdiction cannot hear a case, regardless of whether it has personal jurisdiction.
For example, a small claims court might only handle cases involving a certain dollar amount.
3. Original Jurisdiction:
This refers to a court's power to hear a case for the first time.
Most trial courts have original jurisdiction.
4. Appellate Jurisdiction:
This is the power of a higher court to review decisions made by a lower court.
Appellate courts do not retry cases; they review the legal procedures and decisions of the lower court.
5. Exclusive Jurisdiction:
This means that only one court has the authority to hear a particular type of case.
For example, federal courts have exclusive jurisdiction over bankruptcy cases.
6. Concurrent Jurisdiction:
This occurs when multiple courts have the authority to hear the same type of case.
For example, some cases can be heard in either federal or state court.
 8/8/2025, 3:52:40 AM
No.512503192
>>512503328
>>512503398
>>512503524
>>512503526
>>512503535
>>512503606
>>512503652
>>512503695
>>512503992
>>512505247
>>512505539
>>512505673
>>512505738
>>512505849
>>512505964
>>512506126
>>512506633
>>512506838
>>512507229
>>512507254
>>512507404
>>512509107
>>512509167
>>512509279
>>512509306
>>512511000
>>512511545
>>512511606
>>512511897
>>512512481
>>512512552
>>512512696
>>512512785
>>512512924
>>512513010
>>512514057
>>512514894
>>512516065
>>512522516
>>512522664
>>512523484
>>512523842
>>512524712
>>512524714
>>512524892
>>512526616
>>512526695
>>512530344
>>512530591
>>512531534
>>512531953
>>512532279
>>512532334
>>512533643
>>512534449
>>512534587
>>512534698
>>512534852
>>512534892
>>512536109
>>512537781
>>512540872
>>512540928
>>512541018
>>512541242
>>512543814
>>512544135
>>512544434
>>512545023
>>512545533
>>512545801
>>512547146
>>512549000
>>512552957
8/8/2025, 3:52:40 AM
No.512503192
>>512503328
>>512503398
>>512503524
>>512503526
>>512503535
>>512503606
>>512503652
>>512503695
>>512503992
>>512505247
>>512505539
>>512505673
>>512505738
>>512505849
>>512505964
>>512506126
>>512506633
>>512506838
>>512507229
>>512507254
>>512507404
>>512509107
>>512509167
>>512509279
>>512509306
>>512511000
>>512511545
>>512511606
>>512511897
>>512512481
>>512512552
>>512512696
>>512512785
>>512512924
>>512513010
>>512514057
>>512514894
>>512516065
>>512522516
>>512522664
>>512523484
>>512523842
>>512524712
>>512524714
>>512524892
>>512526616
>>512526695
>>512530344
>>512530591
>>512531534
>>512531953
>>512532279
>>512532334
>>512533643
>>512534449
>>512534587
>>512534698
>>512534852
>>512534892
>>512536109
>>512537781
>>512540872
>>512540928
>>512541018
>>512541242
>>512543814
>>512544135
>>512544434
>>512545023
>>512545533
>>512545801
>>512547146
>>512549000
>>512552957