Search Results
7/25/2025, 10:29:13 AM
>>17870225
More like pandemic time.
>Yersinia pestis (Y. pestis; formerly Pasteurella pestis) is a gram-negative, non-motile, coccobacillus bacterium without spores. It is related to pathogens Yersinia enterocolitica, and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis, from which it evolved. Yersinia pestis is responsible for the disease plague, which caused the Plague of Justinian and the Black Death, one of the deadliest pandemics in recorded history. Plague takes three main forms: pneumonic, septicemic, and bubonic. Y. pestis is a facultative anaerobic parasitic bacterium that can infect humans primarily via its host the Oriental rat flea (Xenopsylla cheopis), but also through aerosols and airborne droplets for its pneumonic form As a parasite of its host, the rat flea, which is also a parasite of rats, Y. pestis is a hyperparasite
>Several species of rodents serve as the main reservoir for Y. pestis in the environment. In the steppes, the natural reservoir is believed to be principally the marmot. In the western United States, several species of rodents are thought to maintain Y. pestis
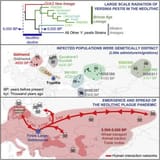
>In 2010, researchers in Germany definitively established, using PCR evidence from samples obtained from Black Death victims, that Y. pestis was the cause of the medieval Black Death
>In 2011, the first genome of Y. pestis isolated from Black Death victims was published, and concluded that this medieval strain was ancestral to most modern forms of Y. pestis
>In 2015, Cell published results from a study of ancient graves. Plasmids of Y. pestis were detected in archaeological samples of the teeth of seven Bronze Age individuals, in the Afanasievo culture in Siberia, the Corded Ware culture in Estonia, the Sintashta culture in Russia, the Unetice culture in Poland, and the Andronovo culture in Siberia. In 2018, the emergence and spread of the pathogen during the Neolithic decline (as far back as 6,000 years ago) was published
More like pandemic time.
>Yersinia pestis (Y. pestis; formerly Pasteurella pestis) is a gram-negative, non-motile, coccobacillus bacterium without spores. It is related to pathogens Yersinia enterocolitica, and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis, from which it evolved. Yersinia pestis is responsible for the disease plague, which caused the Plague of Justinian and the Black Death, one of the deadliest pandemics in recorded history. Plague takes three main forms: pneumonic, septicemic, and bubonic. Y. pestis is a facultative anaerobic parasitic bacterium that can infect humans primarily via its host the Oriental rat flea (Xenopsylla cheopis), but also through aerosols and airborne droplets for its pneumonic form As a parasite of its host, the rat flea, which is also a parasite of rats, Y. pestis is a hyperparasite
>Several species of rodents serve as the main reservoir for Y. pestis in the environment. In the steppes, the natural reservoir is believed to be principally the marmot. In the western United States, several species of rodents are thought to maintain Y. pestis
>In 2010, researchers in Germany definitively established, using PCR evidence from samples obtained from Black Death victims, that Y. pestis was the cause of the medieval Black Death
>In 2011, the first genome of Y. pestis isolated from Black Death victims was published, and concluded that this medieval strain was ancestral to most modern forms of Y. pestis
>In 2015, Cell published results from a study of ancient graves. Plasmids of Y. pestis were detected in archaeological samples of the teeth of seven Bronze Age individuals, in the Afanasievo culture in Siberia, the Corded Ware culture in Estonia, the Sintashta culture in Russia, the Unetice culture in Poland, and the Andronovo culture in Siberia. In 2018, the emergence and spread of the pathogen during the Neolithic decline (as far back as 6,000 years ago) was published
Page 1