FTL1, or ferritin light chain 1, is a protein that plays a crucial role in storing iron within cells and is involved in iron metabolism. Research has shown that increased levels of FTL1 in the brain are linked to cognitive decline and memory loss, particularly in aging. studyfinds.org Wikipedia
Overview of FTL1 Protein
FTL1, or ferritin light chain 1, is a protein encoded by the FTL gene in humans. It plays a crucial role in iron storage and metabolism within cells.
Functions of FTL1
Iron Storage: FTL1 is part of the ferritin complex, which stores iron and helps regulate its levels in the body.
Neuronal Development: It is important for the development of neurons and the synthesis of neurotransmitters.
Detoxification: FTL1 helps remove excess iron, preventing oxidative stress caused by free iron radicals.
Role in Aging and Cognitive Function
Recent research has identified FTL1 as a significant factor in age-related cognitive decline. Increased levels of FTL1 in the brain are associated with:
Memory Loss: Higher FTL1 levels correlate with diminished cognitive abilities and fewer connections between brain cells, particularly in the hippocampus, which is vital for learning and memory.
Reversibility: Reducing FTL1 levels in older mice has been shown to restore memory function and improve synaptic connections, suggesting potential therapeutic avenues for age-related memory impairments.
Clinical Significance
Mutations in the FTL gene can lead to neurodegenerative diseases, such as neuroferritinopathy, characterized by iron metabolism abnormalities and oxidative stress. This highlights the importance of FTL1 in both normal brain function and disease processes.
studyfinds.org Wikipedia
4chan Search
10 results for "49f3e408a9e91df4d4d066b84a6e8c2c"
>>512996254
try and hide the fact they are demonic terrorists
try and hide the fact they are demonic terrorists
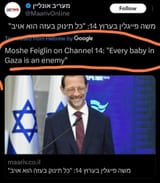
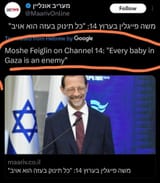
Should babies be considered enemy combatants?
>>512951808
No one is buying that Israeli cool aid except the biggest christcucks imaginable, retarded Zionists and the JIDF shills in /r/world news.
No one is buying that Israeli cool aid except the biggest christcucks imaginable, retarded Zionists and the JIDF shills in /r/world news.
Should babies be considered enemy combatants?
>>213624048
So true Schlomo
So true Schlomo
>You forgot modest and generous.
Can babies shoot guns?
Why are they so cartoonishly evil?